MOSFET or Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor is a type of transistor whose operation depends on the field effect, i.e. the electric field on the Input GATE or the Input Input. MOSFET consists of 3 foot terminals namely Gate (G), Drain (D) and Source (S). MOSFET works electronically varying along the path of the charge carrier (electron or hole). Electric charges enter through the Channels at the Source and exit through the Drain. The width of the channel is controlled by the voltage at the electrode, which is called the Gate which is located between the Source and Drain. it is isolated from channels near the very thin layer of metal oxide. MOS capacity in this component is the main part.
MOSFET has two modes, the first mode is Depletion Mode and Enhancement Mode. In general, MOSFET are used in electronic circuits as Switches, Amplifiers and Mixers. Field Transistors These effects can be classified into 2 types, namely N type MOSFET (N MOSFET) and P type MOSFET (P MOSFET).

MOSFET Example
Explanation of MOSFET Mode
a. Enhancement Mode
When there is no voltage on the Gate, the MOSFET will not be conductive. As the voltage increases at the Gate, the conduction properties of the Channel are getting better.
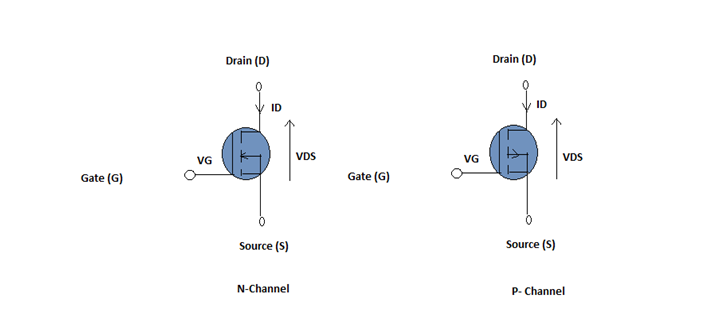
Enhancement MOSFET mode diagram
b. Depletion Mode:
When there is no voltage on the Gate, the channel condition is at its maximum. Because the voltage at the positive or negative gate conduction in the channel decreases.
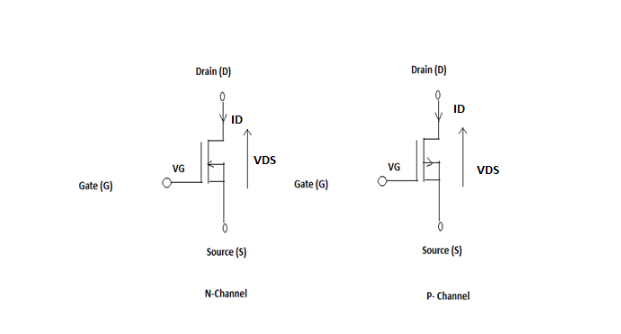
Depletion MOSFET mode diagram
How does MOSFET work?
The main purpose of a MOSFET is to control Voltage and Current through the Source and Drain. This component is almost entirely as a switch. MOSFET work depends on the capacity of the MOS. MOS capacity is a major part of MOSFET. Semiconductor surface in the oxide layer below which lies between the source terminal and the drain. This can be reversed from p-type to n-type by applying positive or negative gate voltages, respectively. When we apply a positive gate voltage, the hole under the oxide layer with disgusting force and load is pushed down with the substrate.
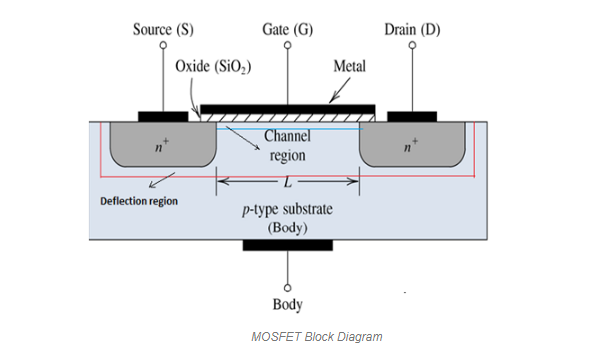
how mosfet works
The depletion region is filled by bound negative charges associated with the acceptor atoms. The electrons reaching the channel are formed. Positive voltage also draws electrons from source n and flows the area to the channel. Now, if a voltage is applied between the drain and the source, current flows freely between the source and the drain and the gate voltage controls the electrons in the channel. Instead of a positive voltage if we apply a negative voltage, channel holes will form below the oxide layer.
P-Channel MOSFET type
P-Channel MOSFET type has a P-Channel area between Source and Drain. He has four terminals such as Gate, Drain, Source and Body. PMOS Transistor structure consists of n-type with Source and Drain regions given P + diffusion.
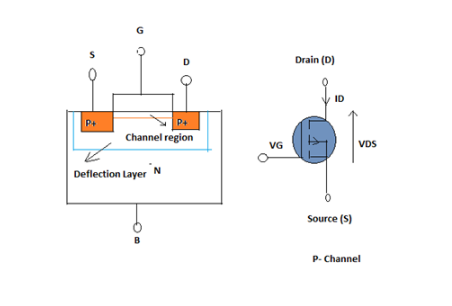
p-channel-mosfet-type
N-Channel MOSFET
The structure of N-Channel Mosfet or called NMOS consists of subtraction type P with Source and Drain areas along with N + Diffusion. Between the Source and Drain regions there is a narrow gap of the P subtraction called the channel covered by an insulator made of Si02.
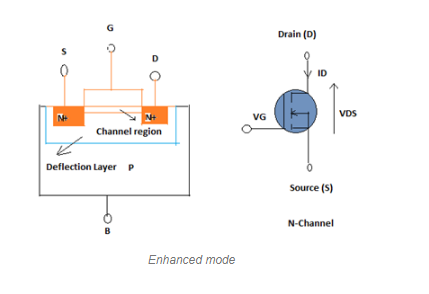
n-channel-mosfet type
Well, hopefully this explanation of MOSFET can help you understand a little about the functions and uses of this small device.



